
An independent person has a mind of their own.
The views, beliefs, ethics and principles of an independent person are well-rooted and hence cannot be easily influenced by the opinions of others.
An independent person makes a decision based on what he/she believes in and not on the expectations or judgements of society.
The lack of insecurity gives an independent person tremendous confidence.
An independent person is open to recommendations, suggestions and advice, but he/she never asks for any help. Their confidence and self-belief give him/her the power to do things on their own.
On, 15th August 2021,
India celebrates its 75th Independence Day.
India is the largest country in South Asia, and, as per area, India is the 7th largest country across the globe.
India comprises of 28 states and 8 territories, making a total of 36 parts.
These 36 entities are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.

The 28 states and their capitals are:
| State | Capital |
| Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| Assam | Dispur |
| Bihar | Patna |
| Chhattisgarh | Naya Raipur |
| Goa | Panaji |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| Haryana | Chandigarh |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| Karnataka | Bangalore |
| Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| Manipur | Imphal |
| Meghalaya | Shillong |
| Mizoram | Aizawl |
| Nagaland | Kohima |
| Odisha | Bhubaneswar |
| Punjab | Chandigarh |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| Sikkim | Gangtok |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| Telangana | Hyderabad |
| Tripura | Agartala |
| Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| Uttarakhand | Dehradun, Gairsain (Summer) |
| West Bengal | Kolkata |
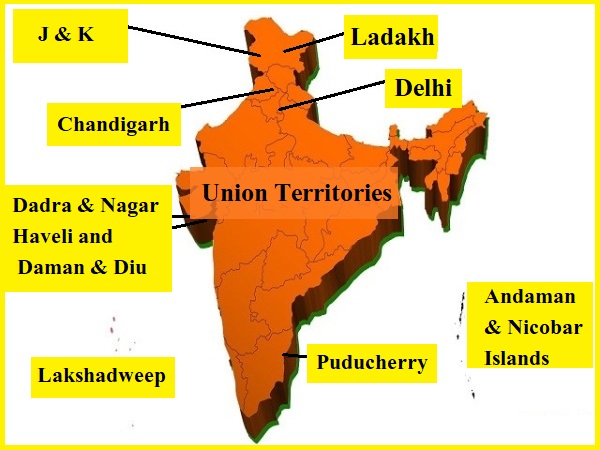
The 8 Indian Union Territories and their capitals are:
| Union Territories | Capital |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| Dadra Nagar Haveli and Daman Diu | Daman |
| Delhi | New Delhi |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer), Jammu (Winter) |
| Ladakh | Leh |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| Puducherry | Puducherry |
The 5 Precious Pearls of Our India are:
A. Landscape
B. Food
C. Language
D. Culture and Traditions
E. Spirituality
A. Indian Landscape

India is a fragment of the continent of Asia.
India is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, in the southeast region, and by the Arabian Sea in the southwest region.
Hence, India is also called the “Peninsula”.
India has every landscape on Earth, that you can think of.
Cold snow-covered mountains, infertile barren deserts, hot and humid plateau, massive plains,
widespread seashores and tropical islands are some of India’s physical features.
Depending on the geographical landscapes, the physical features of India are allocated into 6 types:
1. The Himalayan Mountains
2. The Northern Plains
3. Peninsular Plateau
4. Indian Desert
5. Coastal Plains
6. Islands
- Himalayan Mountains
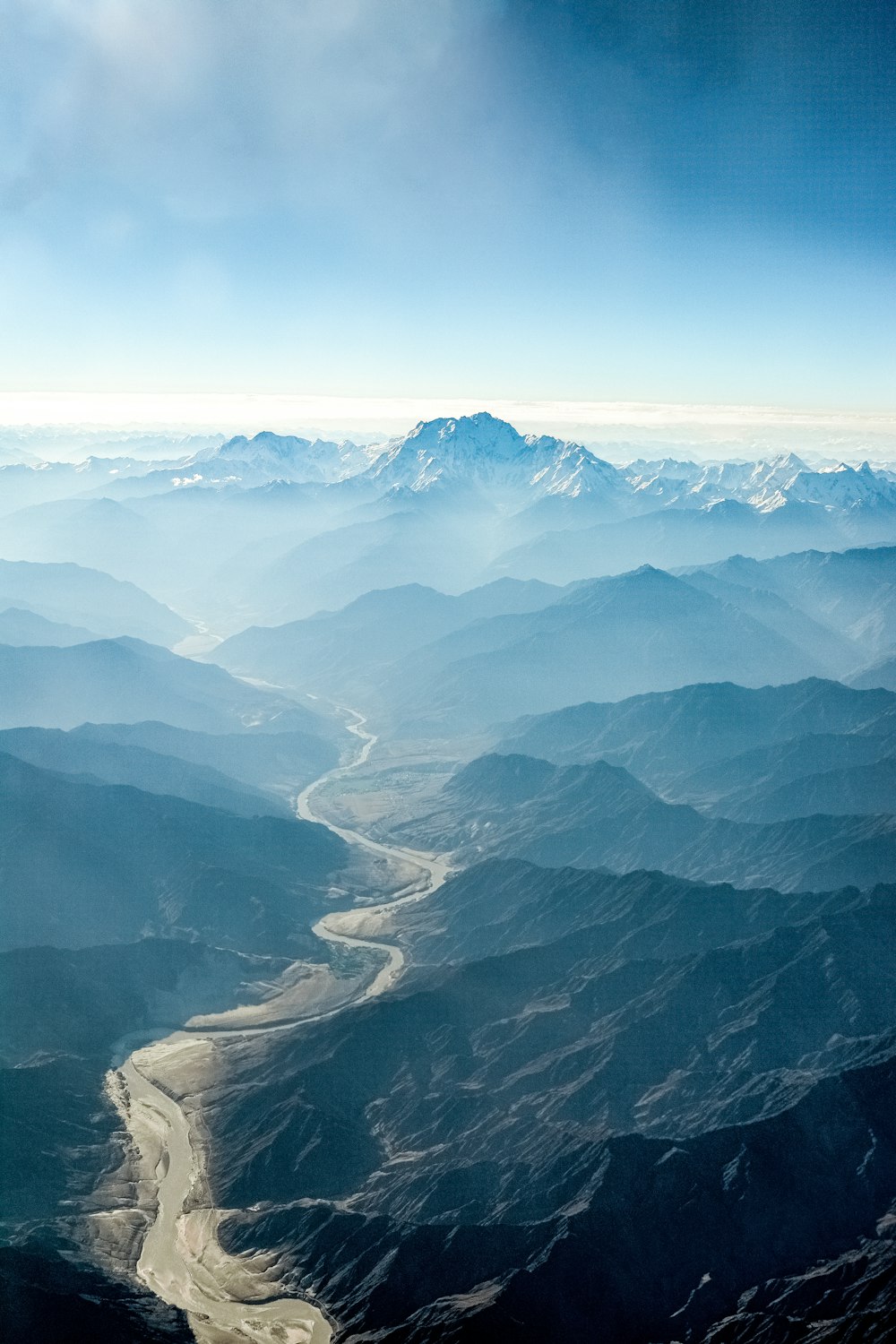

The Himalayas are located in the northernmost part of the country.
The name “Himalaya” is derived from the Sanksrit words, “Hima” means “Snow” and “laya” means “abode”.
“Himalaya” means the “Abode of Snow”.
Over the years, the word “Himalaya” urbanized into the plural form “Himalayas”, because of its vast mountain ranges.
The Himalayan Mountain Ranges are in the shape of an arch. This aids in keeping the “Cold Arctic Winds” from reaching the tropical landmass.
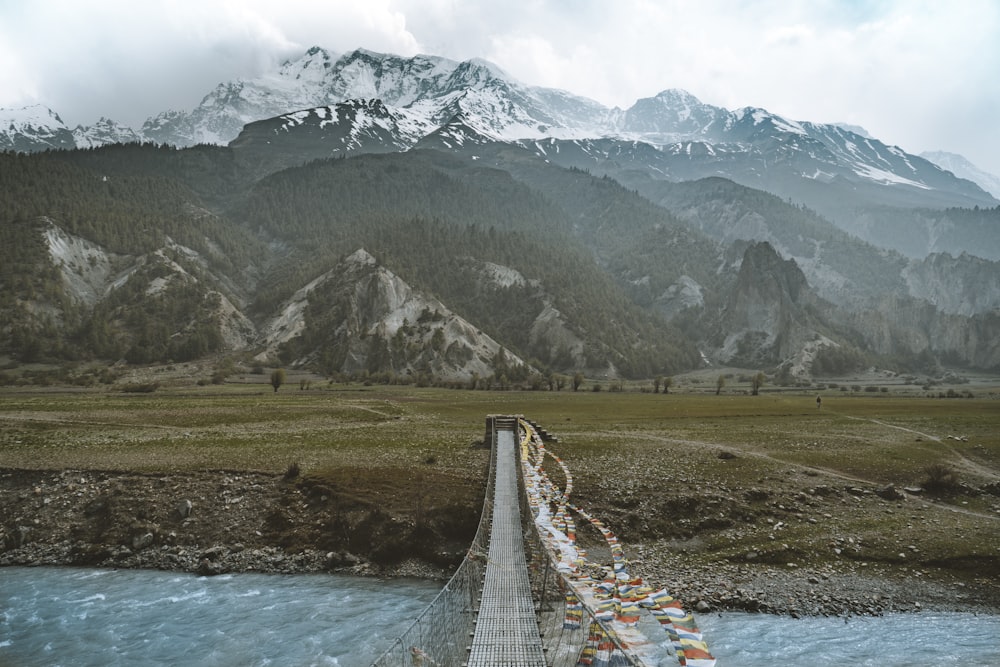

The Indian Himalayan Region ( IHR) dips and dives in and out of the Greater, Lesser and Siwalik Ranges.
The Greater Himalayas, also known as the Himadri. Some of the highest mountains on Earth originate in the Himalayan region. The Great Himalayas is home to Mount Everest. The average peaks of the mountain in this region reach up to 6000 meters above sea level.
The Lesser Himalayas have average peaks rising as high as 4000 meters. The Pir Panjal range, Dhaula Dhar range and Mahabharat range are the prominent ranges of this region. These regions are well known for their hill stations.
The Outer Himalayas is also known as the Siwalik Range, having altitudes varying between 900 and 1100 meters. These ranges are made up of unconsolidated sediments. These sediments were coming down with the flowing rivers of the main northern Himalayan ranges.
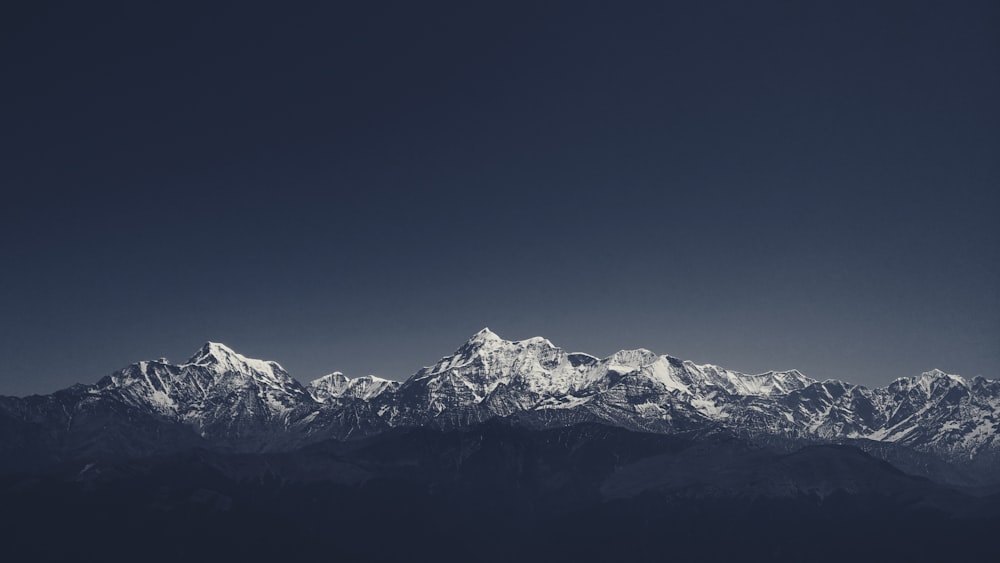

2. Northern Plains
The three major rivers of India are the Indus, Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
These rivers along with their tributaries have emerged from the slopes of the Himalayas.
Since these river basins had huge amounts of alluvial deposits, these regions grew fertile over hundreds of years and led to the development of the Northern Plains.
The Northern Plains is divided into three important parts-
• The Punjab Plains

The Indus River and its tributaries lead to the creation of these vast plains, the main part of which now lies in Pakistan
• The Ganga Plains

These plains spread across the states of North India. The states are – Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Bihar, Jharkhand, Delhi and West Bengal.
• The Brahmaputra Plains

This covers the main regions of Assam and the other North Eastern States.
3. Peninsular Plateau

The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest landform, in India. The “Tectonic shifts” of the “Gondwana Land” resulted in the formation of this plateau.
This enormous plateau region is divided into two sections –
• The Central Highlands –

They are located on the northern side of the Narmada River.
They cover an enormous part of the Malwa Plateau.
• The Deccan Plateau-

Deccan plateau is a triangular landmass. It is located in the southern part of the Narmada River.
The Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats are situated on this plateau’s eastern and western sides, respectively.

The famous “Satpura Range”, is a series of seven mountains (‘Sat’ means seven and ‘pura’ means mountains), is a part of the Deccan Plateau.
4. Indian Desert

On the western fringes of the Aravali Hills, you can see the rising and falling sandy plains of the Indian Desert.
With rainfall as low as 150 mm per annum, this region is the most deserted place in the country. Thus, it is low on greenery.
The north-western parts of Gujarat and most parts of Rajasthan are the desert regions of India.

5. Coastal Plains
The narrow strips of the coastal plains are located on the outer edges of the Indian peninsula.
Coastal plains are the shores of the Bay of Bengal in the East and the Arabian Sea on the West.
The 3 western coasts along the Arabian Sea are the Konkan Coast, near Maharashtra and Goa, Kannada Plains of Karnataka and the Malabar Coast of Kerala.



The Northern Circars and the Coromandel Coast are the Eastern coastal regions of India.

6. Islands
Lakshadweep Island lies closer to the Malabar Coast of India.
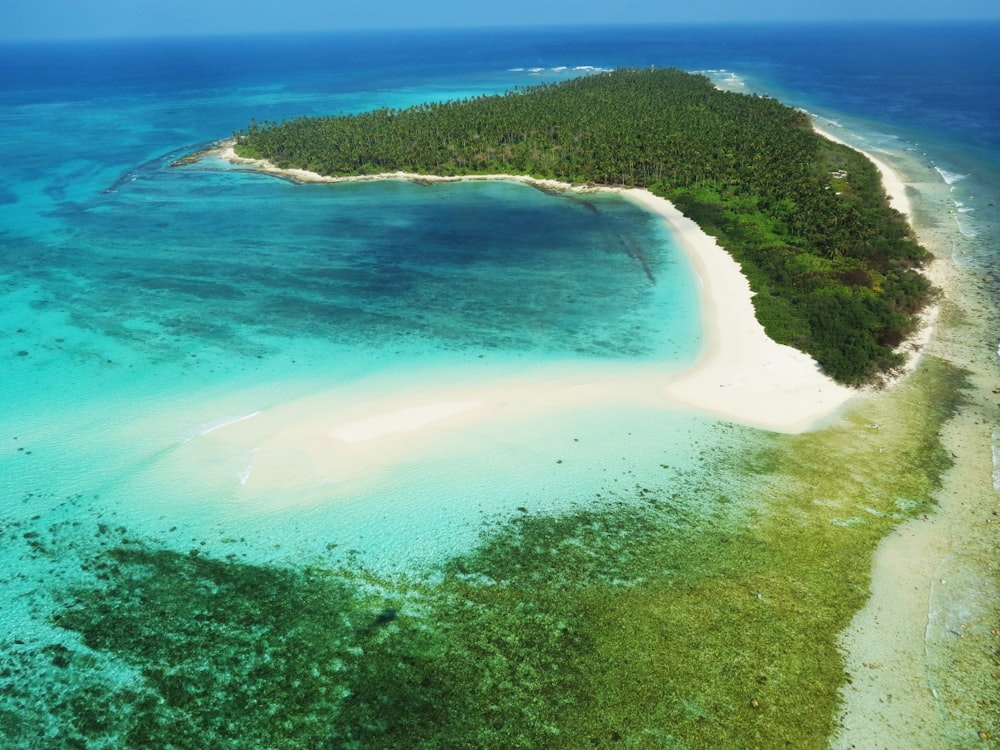

The Andaman & Nicobar Islands lie on the Indian Ocean. Andaman & Nicobar Islands experiences an equatorial climate, as they are situated closer to the equator.

With its vast and varied landscape,
India is one of the best places to travel
and explore nature’s beauty.
As you can see India is vast and diverse so ….TO BE CONTINUED …
Discover more from Dreamz&Experiences
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.


[…] 5 Precious Pearls of Our India […]
[…] 5 Precious Pearls of Our India – Part 1 […]